end tidal co2 meaning
End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a.
Etco2 End Tidal Co2 By Acronymsandslang Com
The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at.

. Obviously the alveolar and arterial CO2 values increase during breath-holding. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45 mm HG. Of or relating to the last portion of expired tidal air End-tidal carbon dioxide monitors are already being used and are recommended to indicate the adequacy of.
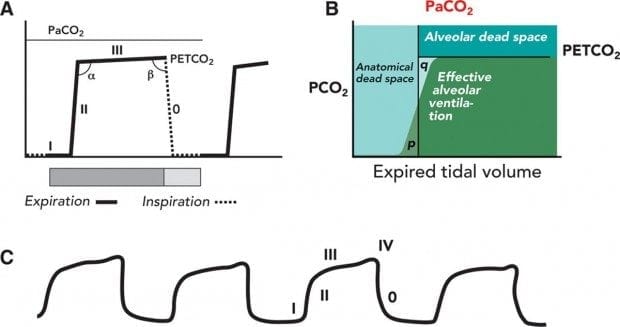
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 is the level of carbon dioxide that is released at the end of an exhaled breath. Of or relating to the last. Figure 1 reviews the meaning of each phase of the waveform.
High ETCO2 helps predict respiratory arrest before a change in mentation and decompensation occur and time to prepare airway equipment. Many things must occur for the exhaled carbon dioxide tracing to appear normal fig. ETCO2 is the amount of carbon dioxide CO2 in exhaled.
End-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a measure of metabolism perfusion and ventilation. Exhaled carbon dioxide both in terms of its quantity and pattern provides detailed information on the cardiopulmonary system. The waveform is called capnograph and shows how much CO 2 is present at each phase of the respiratory cycle.
2 Its useful to keep these terms. There is more than one version of this tool. There are Capnometers which display a numeric reading of the CO2 Waveform Capnography which creates a graph of the CO2 as well as certain aspects about how the patient is breathing and.
Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status. In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. This is a major respiratory symptom.
45 In this way your EtCO 2 reading can help you better interpret the validity and meaning of. End-Tidal CO2 monitors do exactly as the name implies they monitor CO2 in the air that we breathe out. ETCO2 levels reflect the adequacy with which carbon dioxide CO2 is carried in the blood back to the lungs and exhaled.
In the awake adult normal cardiac index lies between 25-4 Lminm2 with an ETCO2 of 35-45 mmHg. The amount of CO2 at the end of exhalation or end-tidal CO2 ETCO2 is normally 35-45. One may also ask what does low etco2 mean.
Both end-tidal CO2 monitors and pulse oximetry devices work closely together to help monitor the respiratory status of a patient. EtCO2 represents the amount of carbon dioxide at the end of exhalation. If a person has a very shallow breathing pattern with the tidal volume as his dead.
End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation. Capnography however reflects both a number EtCO2 in mm Hg and a waveform. MONITORING of end-tidal carbon dioxide is one of the most important means of determining the physiologic well-being of anesthetized patients.
End-tidal carbon dioxide. 1 ACLS guidelines define high quality chest compressions as. In fact its commonly called the ventilation vital sign.
NaHC03 will increase EtCO2 because it splits into CO2 and H20 So if rises after NaHCO3 do not misinterpret as ROSC Vasopressors will decrease ETCO2 they cause high afterload increasing BP and myocardial blood flow but a decrease in cardiac output. Medical Definition of end-tidal. Available evidence has established that ETCO2 measurement can provide an indication of cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow24 Non.
End-tidal CO2 monitoring is a non-invasive way to monitor a patients carbon dioxide levels. If a person holds his breath the etCO 2 reading is going to show zero no CO2 exhaled. End-tidal carbon dioxide ETco 2 monitoring provides valuable information about CO 2 production and clearance ventilation.
ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical. This causes CO2 to accumulate in the lungs and more of it to be excreted with each breath hypercapnea which would cause the ETCO2 level to rise. Monitoring capnography waveforms and end-tidal CO2 biofeedback during breathing exercises.
Definition of Low CO2 hypocapnia Hypocapnia hypocapnea also known as hypocarbia is defined as a deficiency of carbon dioxide in the arterial blood. CO2 is a byproduct of cellular metabolism which gets transported in the blood to the lungs for elimination. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
For this reason the accuracy of the partial pressure of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 measurements is questionable. We experimentally examined the reliability of ETCO2 measurements through a nasal cannula and found that they depended on both biological factors tidal volume and respiratory rates and mechanical factors the diameter and the. Also called capnometry or capnography this noninvasive technique provides a breath-by-breath analysis and a continuous recording of ventilatory status.
Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood. End tidal CO 2 monitoring is represented as a number and a graph on a monitor. Capnography is the monitoring of the concentration or partial pressure of carbon dioxide CO 2 in the respiratory gasesIts main development has been as a monitoring tool for use during anesthesia and intensive careIt is usually presented as a graph of expiratory CO 2 measured in millimeters of mercury mmHg plotted against time or less commonly but more usefully.
What does high end tidal co2 mean. But CO2 levels are normal or low it may mean that the patient has a cardiac-related problem such as congestive heart. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function.
On average during CPR if adequate chest compressions are being delivered a cardiac index of 16-19 Lminm2 can be generated which correlates with ETCO2 pressures of 20mmHg. End Tidal CO 2 6 Can also be measured and monitored in spontaneously. The number is called capnometry which is the partial pressure of CO 2 detected at the end of exhalation ranging between 35 - 45 mm Hg or 40 57 kPa.
Remains locked to the hemoglobin.

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Normal And Abnormal Capnography Waveforms Infographic Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

Potential Applications Of Capnography In The Prehospital Setting Journal Of Paramedic Practice

The Impact Of Ventilation Rate On End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Level During Manual Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Resuscitation

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

How To Read And Interpret End Tidal Capnography Waveforms Emsuk Learning
End Tidal Co2 The Drummer Of The Vital Sign Band Pem4
Riding The Wave Of Capnography Understanding Etco2 Vetbloom Blog
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
The Normal Capnograph Waveform Deranged Physiology
End Tidal Co2 Monitoring In The Pre Hospital Environment More Than Just Endotracheal Tube Placement Confirmation Journal Of Paramedic Practice

Exhaled Carbon Monoxide End Tidal Co2 And Peripheral Oxygen Saturation Download Table

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Educationcapnography In The Ed Emdocs Net Emergency Medicine Education
